Vaccine Temperature Monitoring Systems - CDC Approved
The proper cold storage of vaccines is crucial to maintain the effectiveness of those vaccines. Vaccine quality is the responsibility of everyone who handles vaccines from the time it’s manufactured, through transit, to the time it’s administered to the patient. The CDC has strict cold chain requirements in order to ensure that vaccines are maintained and distributed in a temperature-controlled environment, ensuring optimal conditions.
How E-Control Systems Works for Vaccine Storage Monitoring
E-Control Systems offers a solution for vaccine storage monitoring and handling. Our wireless sensor network continuously monitors critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, providing real-time data to a centralized system. Instant alerts are triggered if any parameter deviates from the acceptable range, enabling prompt action to prevent potential damage to the vaccines. The vaccine monitoring system logs and stores data for comprehensive historical records and generates detailed reports for compliance with regulatory guidelines. Remote access capabilities allow authorized personnel to monitor and manage vaccine storage environments from anywhere. E-Control Systems supports compliance with strict temperature and storage requirements, ensuring vaccines are stored under optimal conditions and contributing to successful vaccination efforts and public health.
E-Control Systems Features for Vaccines
What makes E-Control Systems stand out? Our sensors and intelligates can monitor any aspect of your Vaccines business 24/7.
What Sets Our Vaccine Temperature Monitoring Devices Apart from Other Options in the Market?
E-Control Systems stands out in the market for vaccine monitoring due to its comprehensive approach, covering all critical environmental parameters necessary for vaccine storage, including Vaccines for Children (VFC). This ensures optimal conditions to maintain the efficacy and integrity of vaccines. The real-time monitoring capabilities and instant alerts provide a proactive approach, allowing immediate action to be taken in case of any deviations. This prevents potential damage to the vaccines and ensures their effectiveness.
The vaccine monitoring system offers advanced features such as data logging and reporting, enabling comprehensive historical records and detailed compliance documentation. The remote access feature allows authorized personnel to monitor and manage vaccine storage environments remotely, facilitating quick decision-making and intervention. With a strong emphasis on accuracy, reliability, and compliance support, E-Control Systems provides a superior vaccine monitoring solution, ensuring the safety and efficacy of vaccines and supporting successful vaccination efforts.
Our Vaccine Storage Monitoring Customers Include:
Vaccine Temperature Monitoring Systems & Devices
The Pfizer vaccine needs to be stored at -70℃ or even colder until just before it is prepared for use. It must remain frozen from the time it is manufactured and shipped to the dispensing location where injections are given.
After creation at Pfizer the vaccines are transferred from the -80℃ storage freezers in the factory to shipping containers packed with dry ice and insulation to keep the vaccines frozen during shipment. The dry ice inside the shipping containers typically last about five or six days, which more than enough time for the vaccine to safely travel to the location where the injections are actually given to patients. The shipping containers have temperature sensors that ensure the vaccines are kept below -70°C during their transit. The vaccines are taken out of these containers and placed into ultra-cold freezers that are -80°C or less.
It is essential to have have a remote temperature monitoring system anywhere these vaccines are stored. This is needed to confirm the vaccines are continuously kept below -70°C until they are ready to be administered to patients or shipped elsewhere.
Most hospitals and medical facilities have ultra-cold freezers, but recent issues with vaccine temperature storage tell the story of undetected freezer failures attributed to various causes. These freezer issues will be easily detected with a remote temperature monitoring system in place. The system should notify key personnel immediately and repeatedly if there is a temperature issue.
Murphy’s law states it. Power failures and cold storage unit malfunctions can ruin vaccines. Backup generators are essential to keep vaccines at a proper temp during a power failure. Temperature monitoring will give you valuable time during any such situation so that you can keep your vaccines at the proper temp.
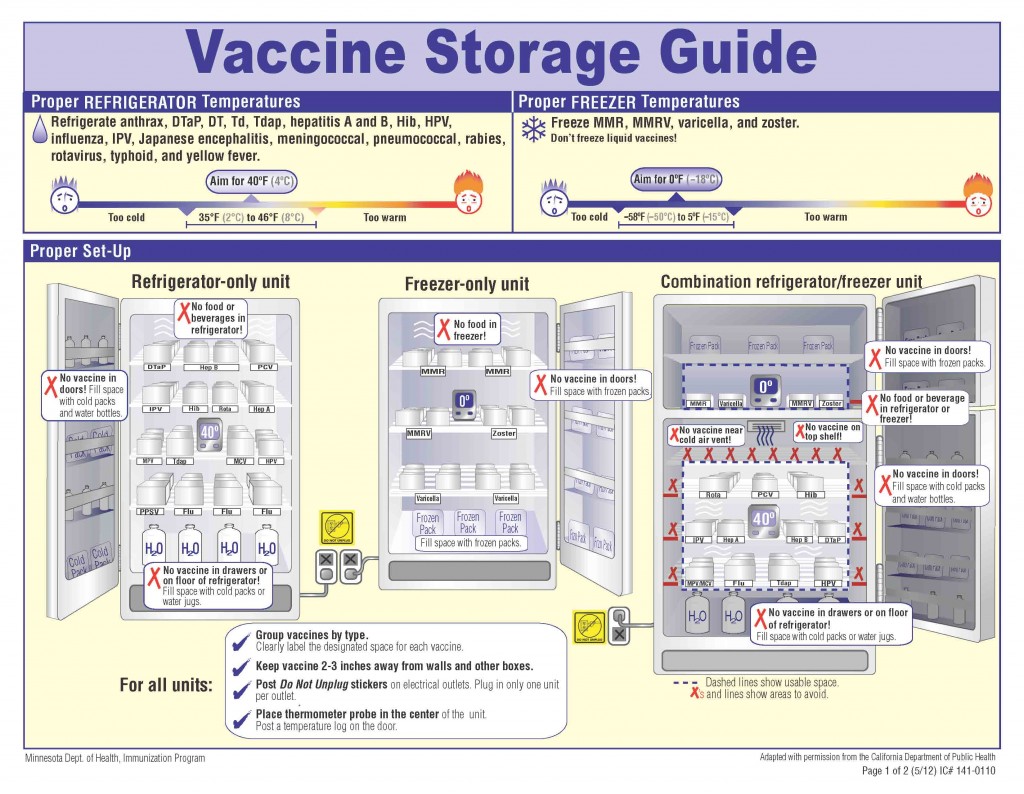
Cold Storage
Household or “dorm-style” refrigeration units are prohibited for the storage of vaccines. This is because they are not good in maintaining consistent internal temperatures. Only pharmaceutical-grade units, equipped with fan-driven air circulation or cold air vents should be used. The purpose of these units are to maintain the required temperature for vaccines, as well as ensure a fast temperature recovery after warm air has entered the cold storage unit.
Freezing Temperatures
Freezing is by far the most devastating issue, especially to the potency of a vaccine, and usually renders them completely useless. Vaccines should be stored at a consistent temperature between 36 and 46 degrees F, and the CDC recommends using a temperature monitoring device to alert you if the temperature of your cold storage unit drops below this.
Disposal
Always dispose of expired or damaged vaccines. Failure to do so contributes to a disorganized environment in your lab that could result in someone receiving a bad vaccine. Expired vaccines also take up space in your cold storage unit, and will hinder airflow, causing the rest of the vaccines to not reach proper temp.
Supply Chain Temperatures
Any staff receiving vaccine shipments should be trained to inspect and properly place the vaccines into their proper cold storage unit right away. Vaccines should be unpacked before placement in the cold storage unit. This is because the packaging that keeps the vaccines at proper temp may cause them to be too cold in the cold storage unit.
Preparedness
Murphy’s law states it. Power failures and cold storage unit malfunctions can ruin vaccines. Backup generators are essential to keep vaccines at a proper temp during a power failure. Temperature monitoring will give you valuable time during any such situation so that you can keep your vaccines at the proper temp.
Air Circulation
Temperature depends on the ability of air to circulate in your cold storage unit. Issues such as overloading cold storage units will cause temperature instability. The proper size cold storage solution is essential, and each vaccine should have space in-between to allow for airflow.
Maintenance
Cold storage units, as well as temperature monitoring devices, need regular inspections and maintenance in order to operate properly for vaccine storage. Cleaning is also very important in the effectiveness of these units, and all parts should stay free of mold, build-up, or any other debris.
Vaccine Cold Storage Temperature Monitoring Device System
The proper cold storage of vaccines is crucial to maintain the effectiveness of those vaccines. Vaccine quality is the responsibility of everyone who handles vaccines from the time it’s manufactured, through transit, to the time it’s administered to the patient. The CDC has strict cold chain requirements in order to ensure that vaccines are maintained and distributed in a temperature-controlled environment, ensuring optimal conditions.
CDC Vaccine Temperature Monitoring
Retail pharmacies main responsibility and primary concern in maintaining the cold chain, lies with the storage and handling of the vaccines while at their facility. The CDC lays out guidelines that were designed to ensure optimal conditions.
Refrigerated vaccines should be stored at temperatures between 2° C and 8° C (36° F and 46° F), with the thermostat set to about 5° C (40° F),which decreases the likelihood of temperature excursions. Vaccines that should be refrigerated include, Influenza (LAIV, IIV, RIV), Hep A, meningoccal containing, HepB, Rotavirus (RV1 and RV5), Human Papilloma Virus (HPV4 and HPV2).
Vaccines stored in the freezer should maintain temperatures between -50° C and -15° C (-58° F and +5° F), with the thermostat set at a midpoint between these temperatures, to assure appropriate frozen temperatures. Some vaccines that should be stored in freezer units include MMR, HZC, VAR, MMRV.
CDC Data Logger Requirements
In order to protect stored vaccines, it’s critical to have accurate temperature history that reflects actual vaccine temperatures. CDC recommends the use of a continuous monitoring and recording digital data logger (DDL). The DDL should have a current and valid Certificate of Calibration Testing, and set to record temperatures at least every 30 minutes, at a minimum. Many DDLs use a buffered temperature probe, to match vaccine temperatures more closely than standard thermometers, which reflect air temperature.
Facilities should have a DDL for each vaccine storage unit and at least one backup DDL, in case the primary one malfunctions or is out for calibration testing. CDC recommend DDLs with the following characteristics:
- Detachable probe in a thermal buffer material like glycol
- Alarm for all out of range temperatures
- Low battery indicator
- Current, minimum, and maximum temperature display
- User programmable logging interval
- Time stamp for when measurement was taken
The CDC does not recommend using alcohol or mercury thermometers, bi-metal stem temperature monitoring devices, food temperature monitoring devices, chart recorders, infrared temperature monitoring devices, and temperature monitoring devices that do not have a current and valid Certification of Calibration Testing.
CDC recommends performing the following routine maintenance tasks for all storage units: Check storage unit door seals for sign of wear and tear, check door hinges and adjust so door opens and closes smoothly, clean coils and motor, clean inside of units, defrost freezer when frost exceeds 1 cm or follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Calibration testing of temperature monitoring device should be done every 1-2 years.
With CDC requirements becoming more strict, it’s now more important than ever to make sure that your pharmacy is up to date with the latest tools to ensure that you are in compliance. Don’t expend your resources on things that you can automate. Let E-Control Systems (ECS) help you with your cold storage monitoring at your facilities, so that you can comply with the CDC recommendations and requirements.
Resources on Proper Vaccine Storage and Handling
- Keys to Storing and Handling Your Vaccine Supply
Decrease vaccine storage and handling errors and preserve the nation’s vaccine supply by demonstrating to immunization providers the recommended best practices for storage and handling of vaccines. (Video is a winner of the Winter/Spring 2014 Web Health Award). - These storage and handling fact sheets illustrate best practices for both refrigerated and frozen vaccines. Written in plain language, they include assessments to reinforce key points. While they are CDC-developed and branded fact sheets, each contains an area where you can insert your agency’s logo.
- Temperature Monitoring Best Practices for Refrigerated Vaccines [2 pages] (Feb 2018)
Fahrenheit (F)pdf icon | Celsius (C)pdf icon - Temperature Monitoring Best Practices for Frozen Vaccines [2 pages] (Feb 2018)
Fahrenheit (F)pdf icon | Celsius (C)pdf icon - Storage Best Practices for Refrigerated Vaccines [2 pages] (Feb 2018)
Fahrenheit (F)pdf icon | Celsius (C)pdf icon - Storage Best Practices for Frozen Vaccines [2 pages] (Feb 2018)
Fahrenheit (F)pdf icon | Celsius (C)pdf icon
- Temperature Monitoring Best Practices for Refrigerated Vaccines [2 pages] (Feb 2018)
- Vaccine Storage and Handling Toolkit
A comprehensive resource for health care providers on vaccine storage and handling recommendations and best practice strategies. The Toolkit includes guidance on managing and storing vaccine inventory, using and maintaining storage unit and temperature monitoring equipment, preparing for emergency situations, and training staff. - You Call the Shots: Vaccine Storage and Handling Module
An interactive, web-based module which provides learning opportunities, self-test practice questions, reference and resource materials, and an extensive glossary. Continuing education credit is available. - These example vaccine labels can be used to organize vaccines within the storage unit. Referenced in the storage and handling toolkit.
- Provider’s Role: Importance of Vaccine Admin. & Storage
Includes vaccine administration, timing and spacing of vaccine doses, observation of precautions and contraindications, management of vaccine side effects, etc. - Vaccines for Children Program: Vulnerabilities in Vaccine Management(Jun 2012)
Report and recommendations released by HHS Office of Inspector General following a routine assessment of the Vaccines for Children program. - Handling a Temperature Excursion in Your Vaccine Storage Unit pdf icon[1 page, 508] (Mar 2020)
This document describes immediate corrective actions following a vaccine storage unit temperature excursion. - Packing Vaccines for Transport During Emergencies pdf icon[2 pages] (Aug 2015)
Do you know how to protect your vaccines during equipment failures, power outages, natural disasters? This document illustrates how to pack your refrigerated vaccines during emergency situations to prevent compromising vaccine storage conditions and damage to your vaccine supply.
Additional Resources for Vaccine Storage and Handling
Note: Storage and handling information in previously published CDC documents, including the 13th Edition Pink Book, may be superseded by the materials listed in above section on this page. If inconsistencies are seen, follow newer guidelines in toolkit or more recently dated materials.
- Vaccine Administration and Storage and Handling Resources Guide
- Storage and Handling Best Practices: Hawaii (2018)
Video highlighting Hawaii’s 2016 CDC Childhood Immunization Champion Award winner applying vaccine storage and handling best practices. - Contact Information for State and Local Health Department Immunization Programs
- Immunization Action Coalition
- Storage and Handling Resources
Refrigerator Temperature Logs (Fahrenheit)(Celsius), Freezer Temperature Logs, Checklist for Safe Storage and Handling, Don’t Be Guilty of These Errors in Storage & Handling, Do Not Unplug Sign… - Manufacturer Product Information:
Package inserts
- Storage and Handling Resources
- Pink Book Chapter on Vaccine Storage and Handling
See note above about referencing this document. - National Institute of Standards and Technology: Vaccine Storage and Handling Research
Continuous Cold Chain Temperature Monitoring that Fits Your Needs
E-Control Systems (ECS) offers a complete wireless temperature monitoring solution for the healthcare industry. Our fully automated enterprise-wide solution makes it easy to monitor your entire healthcare operation, so that you can focus on patient care, instead of manually logging critical data that is needed to comply with many standards, including: The Joint Commission, AABB, GMP, FCC, Vaccines for Children (VFC), and FDA.NIST Traceable Calibration and re-calibration is available directly from the factory, or on-site.
What You Get:
Protection of Assets:
With E-Control Systems wireless temperature monitoring you get instant notifications and alerts when there are improper environmental conditions.
Maintains Regulatory Compliance:
E-Control Systems complies with U.S. FDA 21 CFR Part 11 Guidelines so that your data will always meet integrity and reliability standards.
Simplifies Monitoring:
Easy implementation and remote monitoring capabilities reduce the burden on staff and E-Control Systems lets you monitor multiple locations from a single platform.
Provides a Complete Monitoring Solution:
From installation to support, E-Control Systems will close the gaps in your facility’s temperature monitoring.
Benefits of E-Control Systems
Scalable:
From a single vaccine cooling unit to monitoring thousands of units in different locations globally, E-Control Systems scales with the needs of your facility.
Enhanced Visibility:
With real-time alerts you can rest assured that you will always be notified in the event of an issue. E-Control Systems sends automatic alerts a number of different ways based on your critical parameters.
Efficiency:
No more dealing with data manually. E-Control Systems data loggers collect your data and automatically deliver it to the cloud. This saves valuable time and increases staff productivity.
Remote Monitoring:
Cloud-based monitoring allows you to remotely view and monitor environmental data from anywhere in the world twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week.
Optimized Performance:
Identify risks, failures, and opportunities for improvement. You will see measurable ROI for your facility with E-Control Systems after only a few outages and prevention of loss.
To View More of this Article, Click Here.
Vaccine Temperature Monitoring & Storage FAQ's
Why is a Vaccine Cold Chain Temperature Monitoring Necessary?
Proper cold storage is necessary to preserve the effectiveness of vaccines. Ensuring vaccine quality is a shared responsibility among all who handle them, from manufacturing to administration. To maintain this quality, the CDC enforces strict cold chain guidelines to ensure vaccines are stored and transported under controlled temperature conditions, safeguarding their potency until they are provided to each patient.
What Happens When Patients Receive Ineffective Doses of Vaccines?
When patients receive ineffective doses of vaccines, the most significant consequence is that the patient may not develop adequate immunity to the targeted disease, leaving them vulnerable to infection. This can lead to outbreaks of preventable diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates. Ineffective doses may result in the need for revaccination, causing delays in protection and additional healthcare costs. In rare cases, improper vaccine handling could increase the risk of adverse reactions. Ultimately, ineffective doses undermine public health efforts to control and eradicate diseases.
How Many Times in a Day Is Temperature Monitoring of Vaccines Done?
Vaccine temperature monitoring is done at least twice a day, according to CDC guidelines. This ensures vaccines are consistently stored within the required temperature range, helping to maintain their potency and effectiveness. In addition, many storage units use continuous temperature monitoring devices that provide real-time data and alerts if the temperature falls outside the recommended range.
How to Record Vaccine Fridge Temperature
For vaccine fridge temperature monitoring, follow these steps:
- Use a Digital Data Logger (DDL): Ensure the fridge is equipped with a calibrated digital data logger thermometer for vaccine temperature monitoring that is designed for vaccine storage, which provides accurate readings of the current temperature.
- Check and Record Temperatures Twice Daily: Take temperature readings at least twice a day—once at the beginning of the workday and once at the end. Continuous monitoring via a DDL can help track any temperature fluctuations throughout the day.
- Document the Readings: Record each reading on a temperature monitoring chart for vaccines, including the date, time, and temperature, and note any deviations from the recommended range.
- Follow the Required Temperature Range: Ensure vaccines are stored between 2°C and 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for refrigerated vaccines, and note any deviations immediately for corrective action.
- Take Action if Temperatures Are Out of Range: If temperatures fall outside the safe range, take immediate corrective actions, such as moving vaccines to a backup unit, and record the event and actions taken.
Maintaining accurate temperature logs is important for preserving vaccine efficacy.
Which Vaccines Are Heat Sensitive?
Several vaccines are heat sensitive and can lose their effectiveness if not stored properly at the correct temperatures. Some of the most heat-sensitive vaccines include:
- Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV)
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
- Varicella (Chickenpox) Vaccine
- Rotavirus Vaccine (RV1 and RV5)
- Hepatitis A Vaccine
- Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Influenza Vaccine (varies by type)
- Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis (DTaP) Vaccine
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV4 and HPV2)
These vaccines need to be kept within strict temperature ranges between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F) to ensure their potency is preserved. Exposure to heat can compromise their efficacy, leading to ineffective immunizations.
Which Vaccines Need Ultra-Cold Temperature Monitoring systems?
Ultra-cold vaccine temperature monitoring is needed for these:
- Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine: Requires storage at ultra-low temperatures between -80°C and -60°C (-112°F to -76°F).
- Ebola Vaccine (Ervebo): Requires ultra-cold storage at temperatures of -80°C to -60°C (-112°F to -76°F).
These vaccines must be stored in specialized ultra-cold freezers to maintain their stability and efficacy, with continuous temperature monitoring to ensure they remain cold within the required range.
Which Vaccines Should Be Stored in the Freezer?
Vaccines that should be stored in the freezer and set at a temperature between -50°C and -15°C (-58°F to 5°F) for these vaccines:
- MMR
- HZC
- VAR
- MMRV.
The thermostat should ideally be set near the midpoint to ensure the vaccines remain properly frozen.
How Frequently Should Vaccine Thermometers Be Checked for Accuracy?
Vaccine temperature monitoring systems and vaccine thermometers should be checked for accuracy at least once a year through calibration testing, according to CDC guidelines. Calibration ensures the systems and the thermometer provide accurate temperature readings, which are critical for maintaining the potency of vaccines. It's important to recalibrate thermometers or any temperature monitoring device for vaccines
if they have been dropped or are malfunctioning and to use a calibrated digital data logger (DDL) with a certificate of calibration testing for continuous monitoring.
What Is the Most Accurate Way to Measure Actual Vaccine Temperatures?
The most accurate way to measure actual vaccine temperatures is by using a digital data logger (DDL) with a buffered probe. The buffered probe simulates the temperature of the vaccines themselves, providing more accurate readings than standard thermometers, which may reflect only air temperature fluctuations. A DDL continuously monitors and records temperatures, offering precise data that alerts staff to any deviations from the safe temperature range. This method ensures vaccines are stored under optimal conditions while maintaining their effectiveness.
How Long Can Vaccines Be Left Out of the Fridge?
The amount of time vaccines can be left out of the fridge depends on each specific vaccine and their storage requirements, but most vaccines should not be left out of refrigeration for more than 30 minutes to 1 hour. For certain vaccines, like those that are heat-sensitive (e.g., MMR, varicella), even brief exposure to temperatures outside the recommended range (2°C to 8°C) can compromise their potency and efficacy. If vaccines are left out of the fridge, it's important to refer to the manufacturer's guidelines or consult with health authorities to determine if the vaccines are still safe to use. Any temperature excursions need to be documented, and corrective actions should be taken immediately.
What Temperature Do These Vaccines Need to Be Stored at?
Here are the recommended storage temperatures for each of the listed vaccines:
- Diphtheria and Tetanus Toxoid: Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B: Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- Pertussis Vaccine: Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- Rabies Vaccine: Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- Meningococcal Vaccine (Group A and C): (Group A and C): Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- Haemophilus Influenza Type B Conjugate Vaccine: Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
- MMR Vaccines: MMR should be stored frozen at -50°C to -15°C (-58°F to 5°F).
- Varicella Vaccines: Store frozen at -50°C to -15°C (-58°F to 5°F).
- IPV: (Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine): Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F)
For all vaccines, maintaining the correct temperature range is essential for preserving potency and effectiveness.
How to Deal with Potentially Compromised Vaccines
To deal with compromised vaccines, follow these steps:
- Isolate the Vaccines: Immediately separate the affected vaccines from the rest of your vaccine supply and label them as "Do Not Use" until further investigation can be completed.
- Document the Incident: Record all relevant details, including the date, time, duration, and temperature range during the compromise. Include any information on storage conditions or equipment failure.
- Contact the Manufacturer or Health Authorities: Reach out to the vaccine manufacturer or local health department for guidance on whether the vaccines can still be used or need to be discarded.
- Follow Instructions: Based on their recommendations, decide whether the vaccines can be salvaged or if they must be disposed of according to proper biohazard procedures.
- Review and Correct: Identify the cause of the temperature excursion, whether it's equipment failure, human error, or another factor. Implement corrective actions, such as calibrating equipment, updating protocols, or retraining staff, to prevent future occurrences.
Dealing promptly and carefully with potentially compromised vaccines helps minimize health risks and ensures compliance with public health guidelines.
Why Is Remote Temperature Monitoring for Vaccines Important and What Are the Benefits of It?
Remote temperature monitoring for vaccines is important because it ensures that vaccines are stored at the correct temperature continuously at all times, helping to preserve their full potency and effectiveness. Vaccines are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and exposure to incorrect temperatures can compromise their ability to provide immunity for patients, leading to wastage and potential public health risks.
The benefits of using remote temperature monitoring to protect vaccines and public health include:
- Continuous Monitoring: Remote systems provide 24/7 tracking of temperature, ensuring vaccines are consistently maintained within the required range.
- Real-Time Alerts: These systems send immediate notifications if the temperature falls outside the safe range, allowing quick corrective action to be taken to prevent vaccine spoilage.
- Data Logging: Remote monitoring automatically records temperature data, providing detailed logs for compliance with regulatory standards like those set by the CDC.
- Remote Management: Remote access enables authorized personnel to oversee and manage vaccine storage conditions from any location, allowing for swift decision-making and prompt intervention when needed.
- Enhanced Safety: By ensuring vaccines are always stored properly, remote monitoring helps maintain vaccine efficacy while also protecting public health.
Overall, remote monitoring offers a reliable and efficient way to safeguard vaccine storage and ensure both safety and regulatory compliance.
What is the temperature breach for vaccines?
Vaccines are sensitive to temperature changes, and when their storage environments fall out of the safe range of +2°C to +8°C, it damages their structure and affects their ability to protect people from disease. This is referred to as a temperature breach. If their temperature is too low, they can freeze, and if it's too high, it reduces their effectiveness. When either happens, they are typically labeled as unusable. Breaches occur when vaccines are transported, when there’s a power outage, or when equipment fails.
What is the acceptable temperature range for vaccines?
According to the CDC, the acceptable range for vaccine temperatures is between +2°C and +8°C (36°F to 46°F). When a breach occurs, an investigation is triggered and might require that the affected vaccines be discarded. This safeguards public health while protecting the biological integrity and efficacy of vaccines.
Why is ultra-cold vaccine temperature monitoring important?
To maintain vaccine potency and safety, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) sets and enforces rigorous cold chain temperature monitoring standards to ensure temperature-controlled conditions during storage and distribution because vaccines are vulnerable to fluctuating temperatures and can become ineffective or unsafe. Some vaccine manufacturers also recommend that ultra-cold vaccine temperatures be closely monitored because unexpected power outages can cause irreversible spoilage. Using an E-Control Systems temperature monitoring system can provide real-time alerts to authorized employees who can prevent risks by prompting corrective action if the temperature changes. Monitoring temperatures is important for protecting vaccine inventory, complying with official regulations, and supporting the integrity of public health initiatives.
How is temperature-controlled vaccine shipping monitored?
To meet strict regulatory standards, temperature controlled vaccine shipping is monitored with precise tools that keep track of temperature data from departure to delivery. These records are reviewed by official regulatory agencies, vaccine manufacturers, and pharmacy personnel to confirm the cold chain wasn’t interrupted. If any breach occurs, the data reveals it on the audit trail, ensuring only safe, effective doses reach patients. Even brief exposure to improper temperatures can compromise a vaccine’s stability and effectiveness.
Can vaccine storage monitoring systems integrate with existing lab or pharmacy software?
E-Control Systems’ high-performance vaccine monitoring systems are engineered to work with the software that laboratories and pharmacies already use, syncing data automatically so information is accessible. It will easily connect to your existing setup and be accurate and reliable because integration eliminates manual errors and updates data so it's current. No need to switch platforms or juggle between multiple systems, so temperature monitoring is simple, fast, and dependable. Our vaccine monitoring systems also meet regulatory requirements and improve operational efficiency,
How do vaccine temperature monitoring devices alert staff to temperature excursions?
With E-Control Systems vaccine temperature monitoring devices, your staff can receive instant alerts and real-time data when temperature excursions happen. Then they can intervene and address them even from remote locations, so spoilage won’t occur. Businesses can meet full regulatory requirements without stress or guesswork because our systems collect and record data. When they use our E-Control monitoring system, it ensures vaccine management is safer, simpler, and more reliable.
Healthcare
Popular Vaccine Blog Posts