Wireless Greenhouse Temperature Monitoring System
How E-Control Works for Greenhouse Monitoring and Control Systems
E-Control Systems offers effective solutions for monitoring and controlling greenhouses, ensuring optimal growing conditions for plants. Our system utilizes wireless sensors strategically placed within the greenhouse to monitor crucial parameters such as temperature, humidity and light levels, in real-time.
The collected data is transmitted to a centralized system for analysis and action. If any deviations from the desired growing conditions are detected, E-Control Systems triggers instant alerts via email, SMS, or mobile app notifications. This allows for immediate intervention to adjust environmental factors and maintain ideal conditions for plant growth. With its real-time monitoring and instant alert capabilities, E-Control Systems provides a reliable solution for optimizing greenhouse environments and maximizing plant health and productivity.
E-Control Systems Features for Remote Greenhouse
What makes E-Control Systems stand out? Our sensors and intelligates can monitor any aspect of your Greenhouse business 24/7.
What Sets Our Greenhouse Monitoring Apart from Other Options in the Market?
E-Control Systems stands out in the market for greenhouse monitoring due to its reliability and comprehensive features. Our system utilizes wireless sensors strategically placed within the greenhouse to monitor crucial parameters such as temperature, humidity, and light levels in real-time. This enables precise control and optimization of the greenhouse environment for optimal plant growth.
What sets our greenhouse monitoring solution apart is its advanced alert system and data-driven insights. E-Control Systems triggers instant alerts via email, SMS, or mobile app notifications in case of any deviations from the desired growing conditions. This allows for prompt intervention to address any issues and ensure the well-being of plants. Our system offers comprehensive data logging and reporting features, providing a historical record of environmental conditions. This data can be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement, enabling growers to make informed decisions and maximize crop yield and quality. With its reliability, advanced alerts, and data-driven insights, E-Control Systems offers a superior solution for monitoring and optimizing greenhouse environments.
Our Greenhouse Customers Include:
Greenhouse Monitoring FAQs
What Is the Best Way to Monitor Temperature in a Greenhouse?
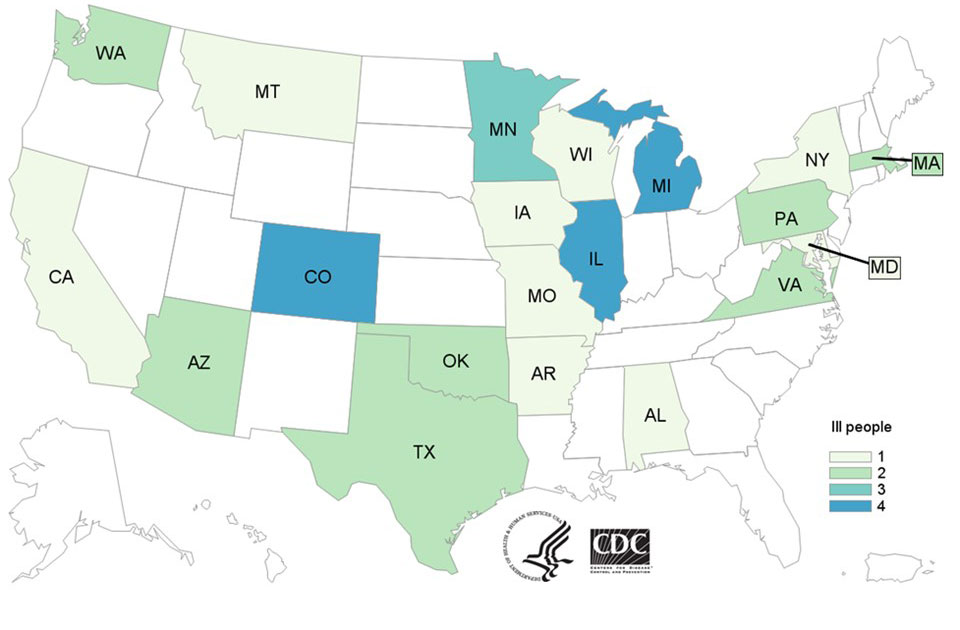
The best way to monitor temperature in a greenhouse is by using a combination of digital temperature sensors and data loggers to provide continuous, real-time readings. Sensors should be placed at locations throughout the greenhouse to account for temperature fluctuations in different zones. Many Greenhouse temperature monitoring systems also include wireless capabilities, allowing you to monitor the temperature remotely via mobile apps or computers. Some Greenhouse temperature monitor systems are equipped with alarms that alert you when temperatures go outside the optimal range, enabling quick adjustments to maintain ideal growing conditions. Regular calibration and maintenance of the sensors are essential to ensure accuracy and consistent monitoring.
What Temperature Sensor Is Used in a Greenhouse?
In a greenhouse, digital temperature sensors are used to monitor and maintain the best growing conditions. These sensors, often combined with thermocouples or thermistors, provide accurate real-time temperature readings. Many greenhouse remote temperature monitors use wireless temperature sensors that can transmit data to a central control system, allowing for remote monitoring and adjustments. Some systems include data loggers to track temperature fluctuations over time, helping growers ensure consistent climate control. Sensors are designed to be durable and reliable in humid and fluctuating environments, making them ideal for greenhouse applications.
Where Do You Put a Temperature Sensor in a Greenhouse?
For accurate readings, temperature sensors in a greenhouse should be placed in several strategic locations. It's best to position sensors at the plant level because this is where temperature variations impact plant growth the most. Place sensors away from direct sunlight, heating vents, or cooling systems, because these can cause inaccurate readings. Distribute sensors evenly throughout the greenhouse, including areas prone to temperature fluctuations, like corners or doorways. For larger greenhouses, multiple sensors should be used to monitor different zones and ensure consistent climate control across the entire space.
How Is the Temperature in a Greenhouse Monitored and Controlled?
Temperature in a greenhouse is monitored and controlled using a combination of temperature sensors and automated climate control systems. Sensors are strategically placed throughout the greenhouse to continuously track temperature levels, and the data is transmitted to a central control system. If temperatures rise or fall outside the optimal range, the system can automatically adjust heating, cooling, or ventilation systems to restore the desired conditions. Growers can also monitor temperatures in real time through remote monitoring tools like mobile apps or computer systems, allowing for manual adjustments if needed. Regular monitoring and control help ensure plants are growing in the ideal environment.
How Do You Control the Temperature of a Greenhouse?
Controlling the temperature of a greenhouse involves using a combination of ventilation, heating, cooling systems, and insulation. Ventilation, such as roof vents or sidewall vents, allows hot air to escape and cooler air to enter, naturally regulating the temperature. Heating systems, like electric heaters or radiant heating, are used during colder months to maintain warmth. For cooling, shade cloths, misting systems, and fans help reduce excess heat. Automated climate control systems, which monitor the temperature in real-time, can adjust these components automatically to maintain optimal growing conditions. Insulating the greenhouse, especially during extreme weather, also helps stabilize temperature fluctuations.
How Do I Know if My Greenhouse Temperature Sensor Is Bad?
You can tell if your greenhouse temperature sensor is malfunctioning by looking for signs of inaccurate or inconsistent readings. If the temperature readings seem erratic or don’t match the actual climate inside the greenhouse, it may indicate a problem. You can test the sensor's accuracy by comparing its readings with a calibrated thermometer placed nearby. If the sensor frequently shows temperature spikes or drops that don't align with the greenhouse environment, it could be faulty. Regular calibration and cleaning of the sensor, as well as checking for any physical damage, can identify and prevent sensor issues. If problems persist, replacing the sensor may be necessary.
How Warm Should a Greenhouse Be at Night?
At night, the ideal temperature for a greenhouse depends on the types of plants being grown, but generally, it should be kept between 45°F to 55°F (7°C to 13°C). For tropical plants or those that require warmer conditions, the temperature may need to be slightly higher, around 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C). Maintaining the right nighttime temperature is essential for plant health because too much cold can slow growth or damage plants, while too much heat can lead to stress. Using heaters, insulation, and greenhouse temperature monitoring systems helps ensure the greenhouse stays within the optimal range during the night.
How do you determine what kind of greenhouse monitoring system and sensors you need?
Determining the appropriate greenhouse monitoring system and sensors involves evaluating several factors to ensure you meet your specific needs. Identify your greenhouse goals, such as climate control, plant health monitoring, or energy efficiency. This will guide your choice of sensors; for example, temperature and humidity sensors are essential for controlling climate and monitoring plant health, while soil moisture sensors help manage watering. Consider the size and complexity of your greenhouse, because larger or multi-zone setups may require more advanced or numerous sensors. Evaluate the types of sensors you need. Integration and automation are also important. Select a system that can integrate with existing climate controls and offer remote monitoring and data analysis. Balance your budget with your needs and choose sensors and systems that are easy to maintain and calibrate for long-term reliability. By addressing these factors, you can select a monitoring system and sensors that best align with your greenhouse's requirements.
How Do You Keep a Greenhouse at a Constant Temperature?
The best way to keep a greenhouse at a constant temperature is by using the best greenhouse temperature monitoring system like the one E-Control Systems offers. Ventilation, heating, cooling, and insulation are also sometimes used. These include:
- Automated Climate Control: Use temperature sensors connected to an automated control system that adjusts heating, cooling, and ventilation based on real-time conditions.
- Ventilation: Install vents, exhaust fans, or sidewall windows to regulate airflow and remove excess heat, especially during warmer days.
- Heating Systems: Use heaters, such as electric or propane heaters, during colder months to maintain warmth. Radiant heating or heat mats can also be used to provide direct heat to plants.
- Cooling Systems: Fans, shade cloths, and misting systems help reduce heat during hot weather. Automated fans and evaporative coolers can provide more precise cooling control.
- Insulation: Insulate the greenhouse with materials like double-glazed windows or thermal screens to retain heat during the night and prevent temperature fluctuations.
A wireless greenhouse temperature monitoring system is better for a greenhouse than relying solely on ventilation, cooling, heating, or insulation because it integrates and optimizes functions for more precise climate management. An automated greenhouse temperature and humidity monitor continuously monitors temperature and humidity levels in real-time using sensors, adjusting ventilation, heating, and cooling automatically to maintain the ideal conditions for plant growth. This ensures more consistent temperatures, reducing the risk of sudden fluctuations that manual systems may miss.
Additionally, automation can save time and energy by reducing the need for manual adjustments, optimizing energy use by only activating systems when necessary, and responding to changes in weather conditions instantly. This uses resources more efficiently and results in healthier plants and higher yields, because the optimal growing environment is consistently maintained.
Can I use my phone as a temperature sensor?
Smartphones don’t have built‑in sensors designed to monitor temperatures, but when you place external wireless sensors around your facility, they can send data to your phone, so it functions like a dashboard, and sends you instant alerts through SMS texts, email, or notifies you through a mobile app when the greenhouse temperature needs to be adjusted.
How does a wireless greenhouse monitoring system simplify setup and scaling compared to wired solutions?
A wireless greenhouse monitoring system significantly saves you time and money because it eliminates the need to run cables, conduits, and trenches. For a wired solution, you need electrical contractors to make sure sensors and data lines are properly installed and protected from moisture. Wireless sensors can be quickly installed using basic mounting hardware and batteries, and placed in a convenient location, making them easy to replace or troubleshoot without affecting the continuous data flow of your entire system. If you want to expand your system, you just add additional sensors and connect them to your network.
What types of alerts are available with the greenhouse temperature alarm function?
The temperature alarm feature allows growers to control growing conditions by receiving real-time alerts through app notifications, emails, and SMS texts, ensuring they receive immediate warnings about temperature variations so they can intervene and protect their crops. Reviewing environmental history allows growers to predict future conditions and make smarter decisions to refine their operations.
How accurate and reliable is the included greenhouse thermometer sensor?
The greenhouse thermometer included with E-Control Systems temperature monitoring system provides reliable, calibrated readings. The data it collects and stores helps manage greenhouse climates and their growing conditions. The sensors generate stable readings in humid environments and refresh data frequently.
What are the key advantages of remote greenhouse monitoring over manual checks?
Remote greenhouse monitoring gives growers a better way to manage greenhouse conditions and allows staff to focus on plant care instead of routine measurements. The system optimizes irrigation, heating, and ventilation while delivering real-time alerts from automated sensors so growers can focus on plant care. This reduces the risk of human oversight and makes scaling up your operations easier, so you won’t need additional labor. The data collected can turn measurements into actionable knowledge and analyze trends to increase harvests and productivity.
Can the wireless greenhouse monitoring system track more than just temperature?
Our E-Control Systems wireless greenhouse monitoring systems can record changes in humidity and monitor CO2, light, and moisture in the soil to prevent overwatering, as well as temperatures to assess growing conditions. Phone alerts and notifications make it easier to react quickly, grow healthier crops, and keep your greenhouse running efficiently year-round.
How do your greenhouse monitoring systems handle power or internet outages to ensure data integrity?
Should your greenhouse lose power or internet connectivity, your data will be safe due to backup batteries and on-site storage. Each of our sensors and gateways has data loggers that store data in case of a network or power outage. When power and internet service return, E-Control Systems will sync your data to the cloud so you’ll never lose important information.