Blood Bank Blood Bank Temperature Monitoring Monitoring
How E-Control Systems Works for Blood Bank
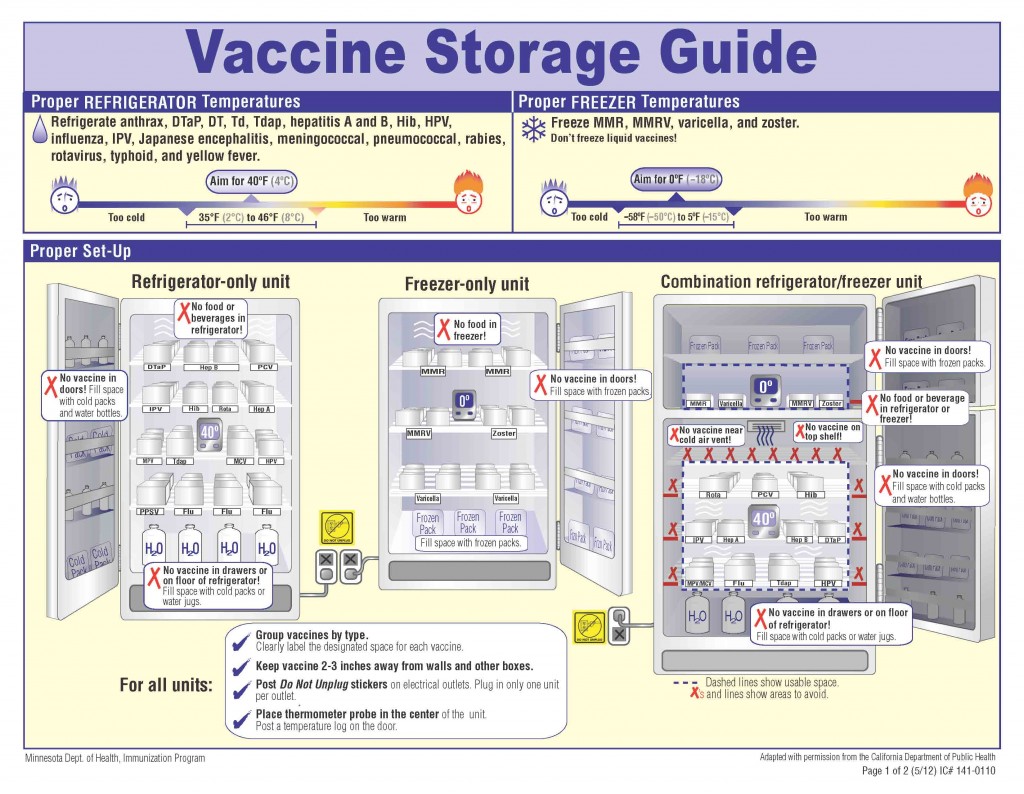
E-Control Systems offers effective solutions for monitoring and controlling blood banks, ensuring the safety and integrity of blood products. Our system utilizes wireless sensors strategically placed within the blood bank facility to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and storage conditions in real-time.
The collected data is transmitted to a centralized system for analysis and action. If any deviations from the desired storage conditions are detected, E-Control Systems triggers instant alerts via email, SMS, or mobile app notifications. This enables prompt intervention to address any issues and maintain the optimal environment for blood storage. With its real-time monitoring and instant alert capabilities, E-Control Systems provides a reliable solution for ensuring the quality and safety of blood products in blood bank facilities.
E-Control Systems Features for Blood Bank
What makes E-Control Systems stand out? Our sensors and intelligates can monitor any aspect of your Blood Bank business 24/7.
What Sets Our Blood Bank Monitoring Apart from Other Options in the Market?
E-Control Systems’ blood bank monitoring solution stands out in the market due to its reliability and comprehensive features. Our system utilizes wireless sensors strategically placed within the blood bank to monitor critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, and storage conditions in real-time. This ensures the preservation and safety of blood products.
What sets our solution apart is its advanced alert system and comprehensive data logging capabilities. E-Control Systems triggers instant alerts via email, SMS, or mobile app notifications if any deviations from the desired storage conditions are detected. This allows for immediate action to address any issues and maintain the optimal environment for blood storage. Our system provides extensive data logging and reporting features, allowing for a historical record of storage conditions. This data can be analyzed for compliance audits, quality control, and process improvement. With its reliability, real-time monitoring, instant alerts, and data-driven insights, E-Control Systems offers a superior option for monitoring and ensuring the safety of blood products in blood bank facilities.