Why Are Hospitals So Cold All The Time?!
Hospitals can be chilly places. Have you ever wondered why hospitals are so cold or if they need to be that cold? There is a reason that they’re kept at an almost uncomfortably cold level. Keeping hospital temperatures cooler makes them better and safer environments. Below are some reasons that hospitals are so cold all the time.
Why Do They Keep Hospitals & ICU Rooms So Cold?
To Prevent Bacteria Growth
Hospitals combat bacteria growth with cold temperatures. Keeping cold temperatures help slow bacterial and viral growth because bacteria and viruses thrive in warm temperatures. Operating rooms are usually the coldest areas in a hospital to keep the risk of infection at a minimum. This is the same premise as food safety practices in the food industry that rely on freezers and refrigeration to keep food bacteria free for customers. This is also why a remote temperature monitoring system is the best way to keep hospitals running at safe temperatures.
Comfort of Hospital Staff
Staff members are constantly moving. For this reason cooler temperatures keep them comfortable. Maintaining a clean environment is critical for patient care, which is why temperatures stay cold, but it is advantageous for staff. Cooler temperatures also mean there will be less chance that hospital staff are sweating, and this in itself can increase safety. Air conditioning also helps to offset the heat bright lights produce during surgery.
Controlling Condensation
Air conditioning naturally takes humidity out of the air. This prevents condensation buildup on surfaces within the hospital. Condensation, which is brought on by humidity and warm temperatures, picks up bacteria and viruses. As condensation moves from surface to surface, it cross contaminates them. To combat this spread of disease and infection in the hospital room, cold temperatures and low humidity prevent condensation on sterilized surfaces, open wounds, and operating equipment.
Cold is Better Than Hot
It’s easier to warm patients up by putting on more layers, extra blankets, and even socks; but keeping patients cool is a harder task. A warm blanket is also comforting, which can help patients feel more calm while in the hospital.
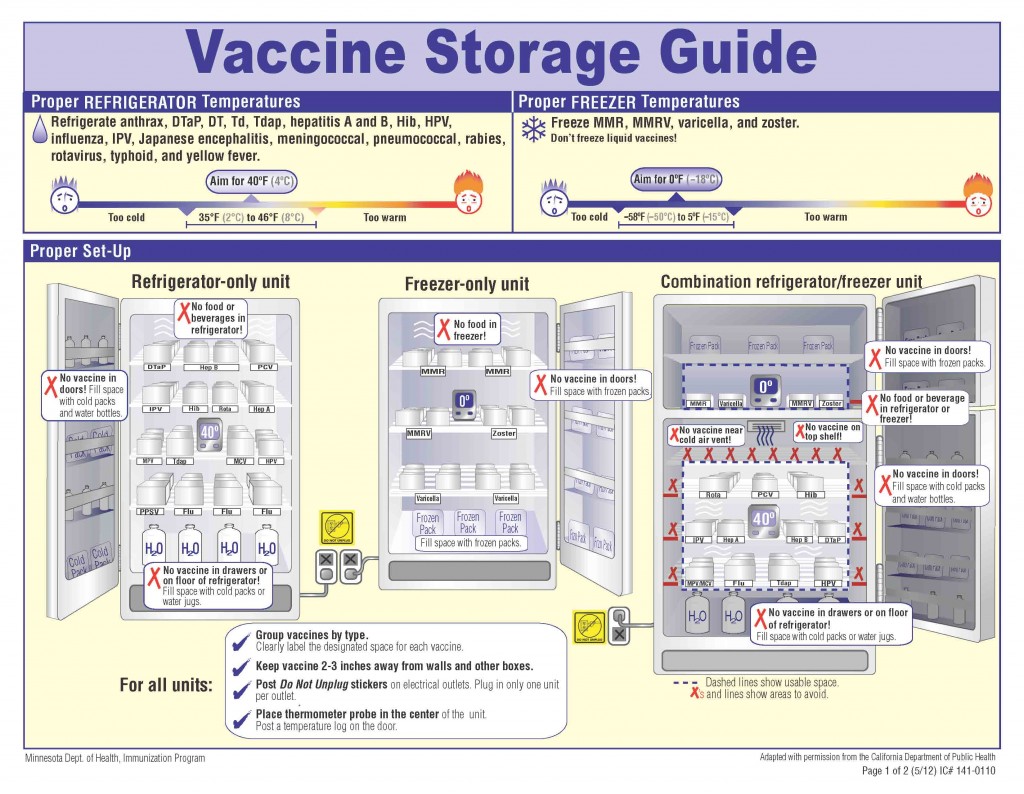
Preserves Medication
Hospital temperature control is critical for preserving medications. Cold temperatures can slow down the degradation process and prolong the shelf life of many types of medications and even blood and tissues for transplants and transfusions. Refrigeration units and climate-controlled storage areas are used to store temperature-sensitive drugs such as vaccines, insulin, and certain antibiotics. Pharmaceutical temperature monitoring within hospitals ensure that medications remain safe and effective.
Hospital Room Temperature FAQ's
What temperature do they keep in hospitals?
Hospital room temperatures are usually kept between 68°F and 75°F to make sure their patients are comfortable, so health risks are minimized and recovery is supported. Operating rooms are often kept at cooler temperatures to eliminate bacterial growth and prevent infection. When the temperature is maintained in the hospital environment to a comfortable level, it helps hospital medical employees stay more focused and alert.
Is every room in the hospital the same temperature?
Areas in the hospital have different temperature needs and depend on the function of each room. Operating rooms have to be sterile to safely perform surgeries and are kept cooler to meet safety requirements, so microorganisms don’t infect patients. Neonatal units accommodate the needs of newborns to keep them warm after birth. Patient room temperatures usually fall between 68°F and 75°F. Blood and medications need exact temperature monitoring to ensure they stay stable and safe.
Why does it feel colder in certain areas of the hospital, like the ER or ICU?
Consistently cooler temperatures are used in some hospital areas like the ICU (Intensive Care Unit) and emergency room, because of their infection control processes. Cooler temperatures are intended to eliminate infectious bacteria and viruses. Another reason is to potentially prevent medical staff from overheating, as they often wear personal protective equipment. A cooler environment and reduced condensation levels are required by some medical equipment located in these two departments, because they often generate heat, which can breed pathogenic microorganisms.
What can I do to prevent getting cold in a hospital?
To stay comfortable when you’re visiting the hospital or admitted as a patient, consider wearing layers of warm clothes, like sweaters, jackets, and thick socks. Requesting additional hospital blankets, which are sometimes heated, might raise your temperature. Drinking hot beverages can warm you up. Ask a hospital staffer if the temperature in your room can be adjusted.
Does a cold hospital environment have any health benefits?
A cold hospital environment provides certain health benefits for patients, visitors, and medical workers. Lower temperatures maintain proper hygiene standards by limiting infectious airborne particles from circulating and create a clean, controlled, sterile setting. Some equipment used for medical testing requires it to be kept at a colder temperature to provide accurate results and function properly. Cool temperatures prevent hospital workers from feeling too hot when they need to wear protective gear and work long shifts. Cold rooms can reduce medical symptoms for some patients. To maintain efficacy and functionality, blood and medication storage areas regulate temperature and humidity levels. By ensuring cleanliness and preventing bacterial growth, cold hospital settings ensure a safer and healthier atmosphere for patients and employees.
Why do some hospitals regulate humidity along with temperature?
Controlling humidity as well as temperature settings in a hospital environment helps maintain safety and sterility. When humidity is balanced to levels between 40% and 60%, it inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria and viruses, and reduces the risk of potential infections in critical operating rooms, ICUs, and other rooms that may be at risk of spreading disease. Maintaining proper humidity prevents electrostatic discharge in medical equipment, which can cause medical equipment malfunctions or failure. Proper humidity levels protect both patients and staff from dryness that may irritate their respiratory systems, eyes, and skin.