How Do Wireless Temperature Sensors Work?
Wireless temperature sensors detect temperature changes and transmit data to a central system without the need for physical wiring. These wireless temperature sensors use built-in thermocouples, RTDs, or thermistors to measure temperature, converting the readings into electrical signals. The data is transmitted through radio frequency, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks to a receiver or cloud-based platform.
Collected data can be monitored in real time, allowing users to set alerts, track fluctuations, and review logs through a wireless temperature monitoring system. This ensures environments, equipment, or products stay within safe temperature ranges. Wireless sensors are powered by batteries or energy-harvesting methods, making them portable and easy to install in difficult-to-reach areas.
Their ability to provide remote, continuous data makes wireless temperature monitoring essential in healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, logistics, and food safety—helping prevent costly temperature-related damage.
What Are Wireless Temperature Monitoring Sensors?
Wireless temperature monitoring sensors are devices that measure and detect heat or temperature changes in an environment or object. They convert temperature readings into electrical signals used to control systems, and then can be monitored, recorded, and transmitted wirelessly. These sensors are essential in healthcare, automotive, manufacturing, and food safety industries, to make sure equipment operates properly and that environments are stable.
What Are Different Types of Temperature Sensors?
Different types of temperature sensors are designed to measure heat and temperature across various applications. Thermocouples are among the most common, using two dissimilar metals that generate a voltage proportional to the temperature difference. Resistance temperature detectors (RTDs) measure temperature by correlating the resistance of the RTD element with temperature changes, providing high accuracy and stability. Thermistors are similar to RTDs but are made of ceramic or polymer materials and generate rapid, sensitive readings over a limited range.
Infrared (IR) sensors detect temperature without direct contact by measuring the infrared radiation emitted by an object, making them work well in hazardous environments. Semiconductor sensors use integrated circuits to measure temperature and are used in consumer electronics. Bimetallic strips are mechanical sensors that bend with temperature changes, commonly used in thermostats. Each type of sensor has unique strengths, making them suitable for various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to food storage and HVAC systems.
Where Can You Use Wireless Temperature Monitoring Sensors?
Wireless temperature sensors can be used in a range of environments to monitor and manage temperature conditions remotely. In industrial settings, they ensure equipment operates within safe temperature ranges, preventing overheating and improving efficiency. In warehousing and storage, they are essential for monitoring temperature-sensitive goods, like pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics, to maintain product integrity.
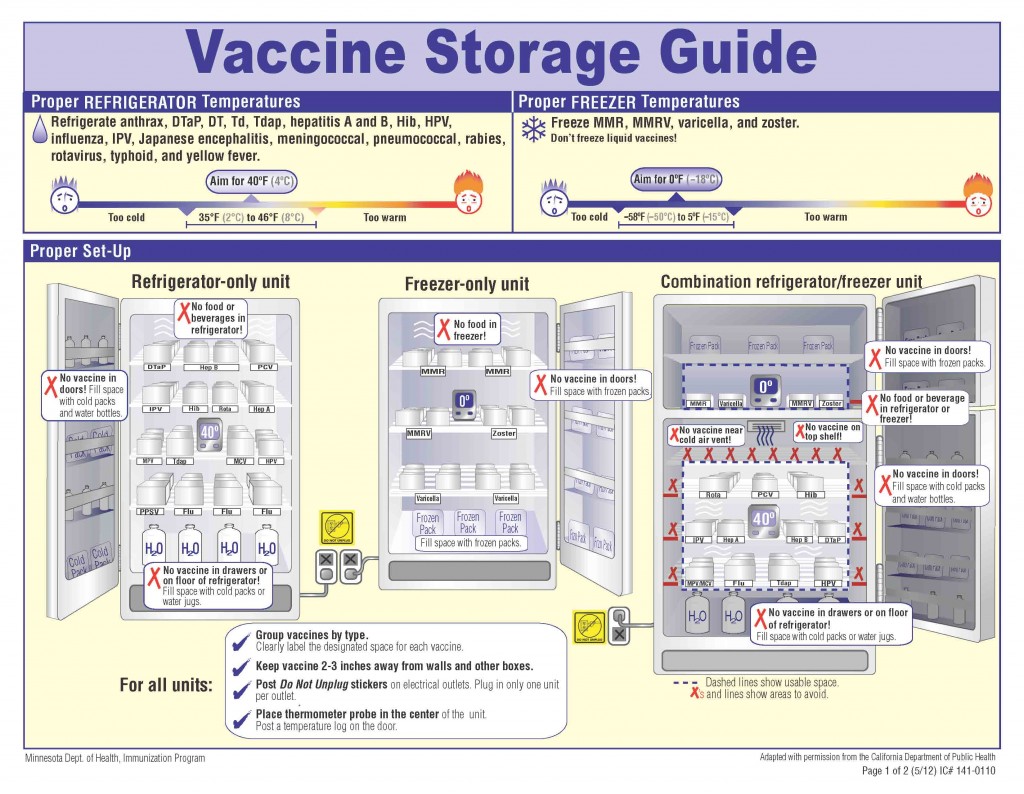
In healthcare, wireless sensors are used to track the temperature of medical storage units, ensuring vaccines and medications are kept at the required temperature. They are valuable in agriculture, where they monitor soil and environmental conditions to increase crop growth. In residential and commercial buildings, wireless sensors work together with smart home systems and HVAC management, improving energy efficiency and maintaining comfort.
Wireless temperature sensors are versatile and can be deployed in environments where wired systems are impractical, providing real-time data and alerts to prevent issues before they develop into bigger problems.
What factors should I consider when choosing a wireless temperature monitor?
When choosing a wireless temperature monitor, consider factors like accuracy and sensitivity to ensure you get precise readings for your specific application. Evaluate the range and connectivity options like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks to ensure reliable data transmission, especially in large or remote areas. Battery life and power efficiency are important for long-term operation and reduce the need for frequent maintenance.
Look for scalability if you need to monitor multiple locations or expand the system over time. Consider alert and notification features that provide real-time warnings when temperature thresholds are exceeded. Data logging and storage capabilities are important for tracking trends and maintaining records for compliance. Finally, assess the monitor’s durability and environmental suitability to ensure it can perform in extreme temperatures or harsh conditions relevant to your specific industry.
How Do You Find the Best Wireless Temperature Sensor for You?
To find the best wireless temperature sensor for your needs, assess the environment and application where you’re going to use it. Consider whether you need it for industrial settings, food storage, healthcare, or home monitoring because different sensors are designed for various conditions. Accuracy and response time ensure precise temperature readings, especially for sensitive applications like food safety or vaccine storage.
Evaluate connectivity options such as Wi-Fi sensors, Bluetooth temperature sensors, or cellular remote temperature sensors depending on range requirements. Look for sensors with real-time alerts and notifications to warn you of temperature fluctuations. Battery life is essential for long-term use and minimizes maintenance. Check if the sensor offers data logging and cloud integration to track temperature trends over time.
Choose a sensor that is scalable and flexible, allowing you to expand your system if needed. Ensure the sensor is durable and suited to the environmental conditions where it will operate, such as in extreme heat, cold, or humidity.
Smart wireless sensors that run on batteries are one of the types of sensors that make up the IntelliSense system from E-Control Systems, which gives users the capacity to track and report a wide range of equipment data. Every IntelliSensor is compatible with the newest Wi-Fi technology. Every IntelliSensor has data logging capabilities that allow it to store data for up to 45 days. The inconvenience and cost of running traditional cables aren’t an issue when you choose battery-operated wireless sensors that can be used almost anywhere.