CDC Refrigerator Temperature Monitoring Guidelines for Vaccines
The ultimate goal of temperature monitoring is to ensure the preservation of safe and effective medications. Given the high cost of many temperature-dependent medications, investing in an effective temperature monitoring system has the potential to deliver significant financial benefits by identifying temperature excursions at the outset, and thus averting product loss.
CDC Vaccine Cold Storage Requirements
The CDC’s Vaccine Storage & Handling Toolkit is a comprehensive document that provides detailed guidance on best practices for cold storage temperature monitoring of vaccines (see www.cdc.gov/vaccines/recs/storage/toolkit/storage-handling-toolkit.pdf). Once these guidelines are put in place to manage vaccine storage, it makes sense to apply them to all medications in refrigerated storage.
Data Capture
The CDC recommends that vaccine storage practices include policies and procedures (P&Ps) for vaccine temperature monitoring. At a minimum, temperatures are to be reviewed and recorded twice per workday. Reviewing the temperatures at least once at the outset of the day and again at the end of the day allows for quick corrective action should a temperature excursion occur.
CDC Refrigerator Recommendations
Further, best practice is to utilize a digital data logger to record and store temperature information at regular intervals over a 24-hour period. This continuous monitoring creates a thorough record of temperature control. The data logger’s digital display should be located outside of the refrigerator or freezer to allow for easy temperature review without having to open the unit or manipulate the probe. Even when alarms are used to indicate out-of-range temperatures, at least two temperature recordings must be recorded daily.
Should a regular temperature recording be missed, the record for that day should be left blank. Anytime a temperature excursion occurs, the event and any actions taken in response should be documented, along with the ultimate outcome. In addition, any mechanical problems, power outages, or repairs performed (with or without an impact on the temperature range) also should be documented.
Data Review
To facilitate ongoing equipment maintenance and satisfy regulatory requirements, pharmaceutical temperature monitoring data must be reviewed weekly. This task should be assigned to the primary or alternate vaccine coordinator. Unless your state has more stringent requirements, temperature data records should be retained for 3 years. Regular review of this data will demonstrate any developing patterns in temperature excursions and indicate when equipment may be in need of repair or reaching the end of its life cycle. Likewise, regulatory inspections will be smoother when the temperature data for a given unit can be quickly accessed to demonstrate system control.
Quick Tips
- Purchase refrigerators and freezers with self-closing doors, and utilize an open door alarm.
- Check the door seal on each storage unit by closing the door on a thin paper slip. If the slip falls or moves easily when pulled, consider replacing the door’s rubber seal. Perform this check all around the door, paying particular attention to the corners.
- If temperature readings never vary within a unit, check the temperature probe to be sure it is functioning properly.
- A buffered probe is the most accurate tool for measuring temperature; temperatures measured in air may be misleading.
CDC Guideline FAQ's
Why Do Vaccines Need to Be Refrigerated?
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines for vaccine storage and handling, to prevent disease and potency loss, vaccines need to be kept within recommended temperature ranges. Vaccines should be stored in a medical-grade refrigerator in an environment that’s consistently cold to ensure they provide reliable immunity. Vaccines are sensitive to environmental factors like heat and moisture. Vaccine preservatives can be compromised when temperatures fluctuate, affecting their safety due to bacterial growth or unwanted chemical reactions. Vaccines can be safely administered when they’re kept at properly regulated temperatures.
What Are the Five Parts of SOP?
HACCP-Based SOPs ensure food safety by integrating these 5 components:
- Identify Hazards: Recognize biological, chemical, and physical risks in food handling and processing.
- Determine Critical Control Points: Pinpoint key stages where hazards can be controlled or eliminated.
- Monitor Procedures: Track food safety measures like temperature and sanitation.
- Implement Corrective Measures: Address deviations to limit food safety risks and maintain standards.
- Maintain Records: Document processes to ensure HACCP and SOP compliance.
What Happens if Vaccines Are Not Refrigerated?
When they aren’t refrigerated, vaccines exposed to high temperatures can become contaminated or degrade, making them unusable. If they’re stored above or below the range that is recommended, the lack of stability might reduce their potency. These issues could make people vulnerable to diseases and infections.
How Do You Store Vaccines in a Refrigerator Safely?
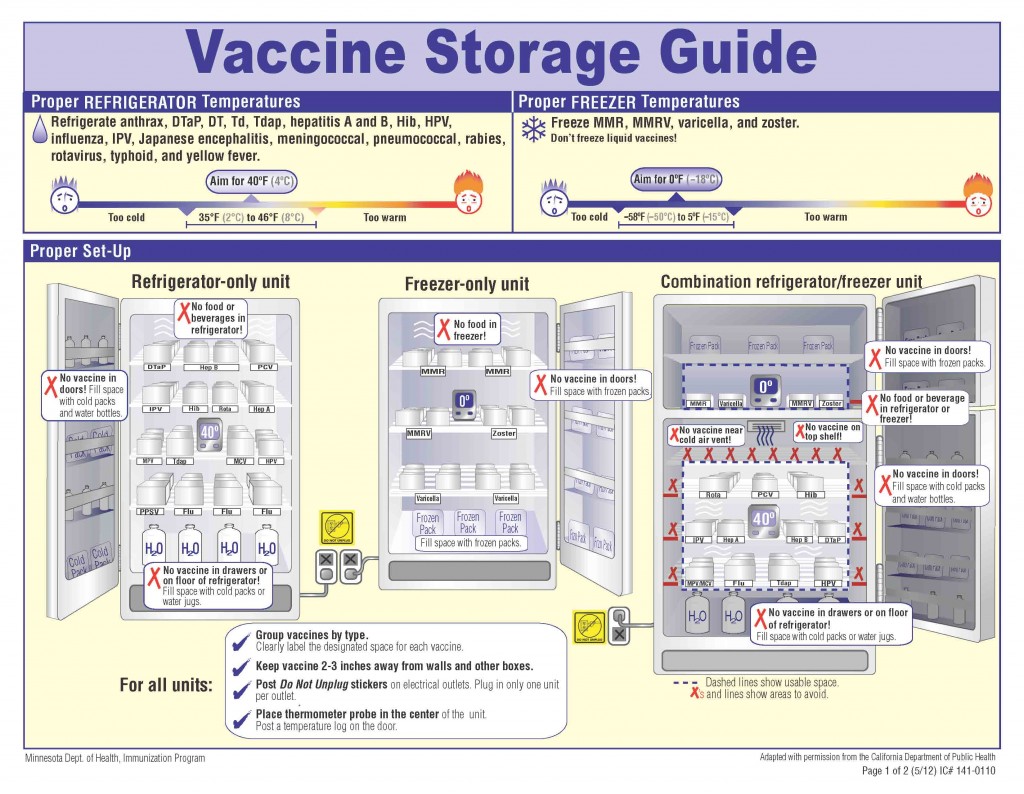
Proper organization inside the refrigerator prevents inconsistencies in temperature, so contamination can be avoided. To store vaccines in a fridge properly, they shouldn’t be placed in the door and should be kept away from walls and vents in the fridge to prevent freezing. Vaccine temperatures should be monitored and recorded so temperature excursions don’t occur that could make them ineffective. Labeled containers or trays allow easy identification.
Do All Vaccines Need to Be Refrigerated?
The vaccine type and its guidelines determine what its proper storage conditions should be. Innovations in developing advanced vaccines have created heat-resistant vaccines that don’t need refrigeration, which are beneficial in areas without cold storage. Most vaccines still need to be refrigerated to ensure they’re safe and effective. Aluminum-based and live vaccines need to be kept at controlled temperatures to maintain their structural integrity and prevent them from degrading.
What Are the Requirements for a Vaccine Fridge?
When you’re using a fridge to store vaccines, store them in their original packaging and keep them away from vents and walls so there aren’t any temperature fluctuations. Food and beverages should be stored in a separate refrigerator from your vaccines to avoid contamination. Select a medical-grade refrigerator with reliable temperature controls, instead of a household model, where temperatures may fluctuate. You can effectively preserve the integrity of vaccines by using a temperature monitoring system from E-Control Systems.
How Long Can Vaccines Be Left Out of the Fridge?
Each vaccine has specific storage requirements, and the time it spends without refrigeration affects its stability and effectiveness. Brief exposure to improper storage temperatures can degrade proteins, causing their components to break down and affecting the level of potency. Healthcare professionals should follow strict protocols about when vaccines need to be discarded because they may be unsafe.
What Temperature Should Vaccines Be Stored At?
A vaccine refrigerator should maintain a stable temperature between 36°F and 46°F and be monitored using a temperature monitoring system to ensure safety. Using a reliable temperature monitoring system will prevent storage errors and ensure medical-grade vaccines stay viable.